Have Waste/Pickup?


Have Waste/Pickup?
E-waste recycling then refers to the reprocessing and re-use of these electronic wastes. It is simple. It is a process that seeks to recover material from electronic waste. This way, you can use them in new electronic products.
Plastic materials may be retrieved and sent for recycling. The recyclers can then use the plastic materials to manufacture items like plastic sleepers and vineyard stakes. You can also get fence posts, plastic trays, insulators, equipment holders, and much more.
Metals can also be retrieved and recycled to manufacture newer steel products and metals.
Devices containing mercury may be sent to recycling facilities using specialized technology to eliminate mercury. The end product of this elimination includes metric instruments, dental amalgams, and fluorescent lighting.
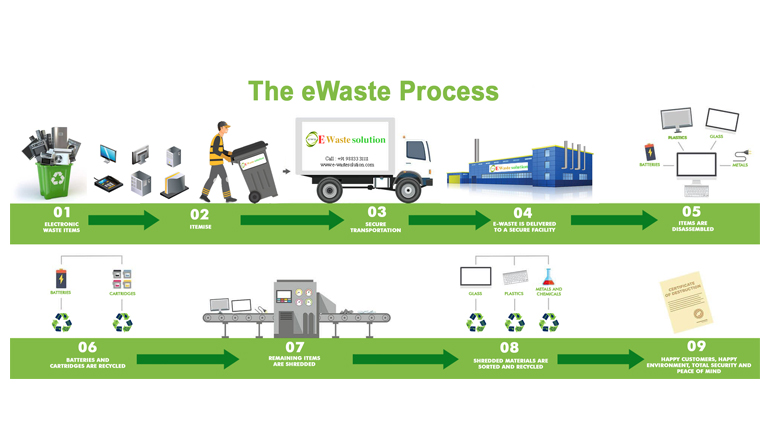
Recycling electronics is an often challenging activity. This is because e-scraps are typically sophisticated and manufactured from diverse elements such as metals, plastics, and glass. While this process often varies, there is a general process. So, here is what you need to know.
This is the first stage of recycling e-waste. Here, recyclers place take-back booths or collection bins in specific places. When these bins get filled, the recyclers then transport the e-wastes to recycling facilities and plants.
After collecting and transporting, the next step is to shred and sort the e-waste. The success of subsequent separation relies on shredding. And this is why efficiency is essential at this stage.
Shredding involves breaking e-waste into smaller pieces for proper sorting. With the use of hands, these tiny prices get sorted and then manually dismantled. This is typically labor-intensive as waste items are, at this stage, separated to retrieve different parts.
After this, the materials get categorized into core materials and components. Then, these items get sorted into various categories. Typically, these category includes items that you can re-use as they are and those that require further recycling processes.
In any case, e-wastes are often manually sorted, while compounds such as fluorescent light, batteries, UPS batteries, and toner cartridges should not be crushed or shredded by hand.
The tiny waste particles get smoothly spread via a shaking process on the conveyor belt. The smoothly spread e-waste pieces then get broken down even further. At this point, the dust gets extracted and discarded in an environmentally compliant manner. This way, there is no environmental degradation.
After this, a strong overhead magnet helps you separate steel and iron from other wastes. This way, you have successfully recycled the steel from the waste stream. However, some mechanical processes may sometimes be required to separate circuit board, copper, and aluminum from other wastes particles. And this is especially where they are mostly plastic.
After this, water separation tech becomes relevant to separate the glass from the plastic. You can then send leads that contain glass to smelters to use in the production of batteries, x-ray tubes, and new CRTs.
The next thing is locating and extracting leftover metals from plastics to purify the waste stream further.
The final stage is preparing recycled materials for sale. Here, the materials separated during SSS get prepared for sale as raw materials to produce new electronics.